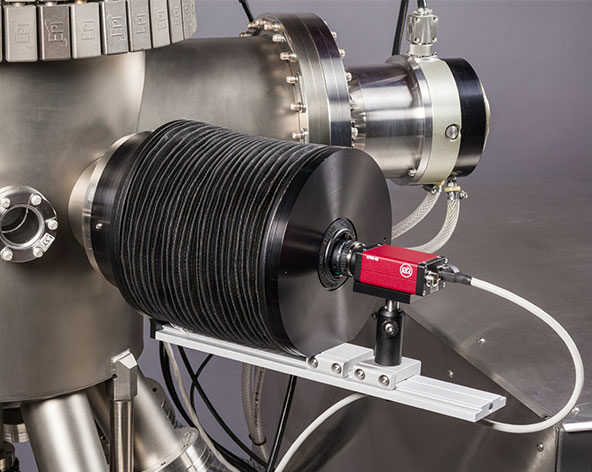
The kSA 400 analytical Reflection High-Energy Electron Diffraction (RHEED) system puts the power of RHEED at your fingertips. Whether analyzing a static diffraction pattern or acquiring data at multiple azimuths during substrate rotation, the kSA 400 makes quantitative RHEED analysis easy. Exploit the power of RHEED with the kSA 400!
The kSA 400 combines a high-resolution, high-speed, and high-sensitivity camera with sophisticated RHEED-specific acquisition and analysis software. This flexible system enables the analysis of virtually any image feature and, with one of many additional options, controls the electron gun for such tasks as acquiring RHEED rocking curves.
Easy to use and straightforward to install, the kSA 400 is designed for convenience and gives quantitative results right out of the box. Seamless integration between hardware and software as well as visually-driven RHEED pattern analysis, makes user operation straightforward and simple. Extensive customer input has helped us make the kSA 400 the industry’s most powerful analytical RHEED system and an integral part of MBE, PLD, PVD, and surface science chambers worldwide. Now in its fifth generation, the goal of the kSA 400 is to provide you with the most information from your RHEED pattern.
Growth Rate
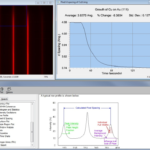
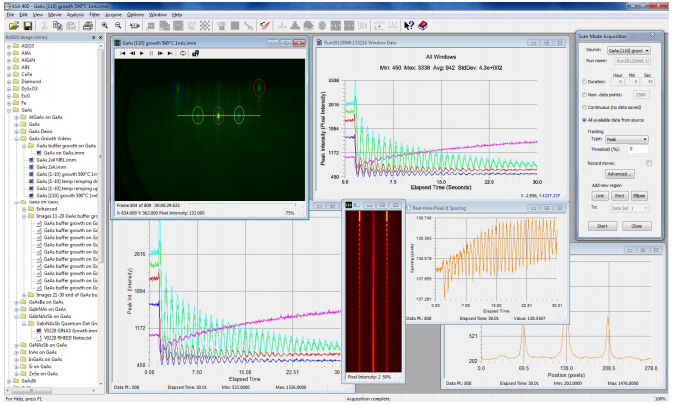
The most common use of RHEED is for determining growth rate via RHEED intensity oscillations, a phenomena that occurs during layer-by-layer epitaxial growth. The kSA 400 determines growth rate via three complimentary methods: Fourier-transform, extrema count (derivative analysis), and damped sine wave fitting. These three techniques determine growth rate independently, resulting in very accurate and consistent measurement of your thin-film growth rate. Watch the kSA 400 monitor RHEED oscillations. For more detailed information see our Growth Rate Methods application note
Lattice Spacing/Strain
Another powerful use for RHEED is to determine the absolute atomic spacing, or lattice spacing, between atoms on a surface. The kSA 400 makes measuring absolute lattice spacing simple. Furthermore, if you’d like to measure the evolution of lattice spacing, or the strain of lattice mismatched growth, the kSA 400 makes this easy too. By monitoring the spacing between diffraction streaks using sophisticated, proven analysis algorithms, strain evolution with very high accuracy and resolution is at your fingertips with the kSA 400.
Structural Analysis
The kSA 400 makes analyzing surface structure easy. By acquiring RHEED images along the major crystal directions of the surface, measuring the pixel spacing and calculating a ratio, surface crystal structure can easily be determined. The kSA 400 also makes acquiring and archiving RHEED patterns a snap. The kSA 400 software contains a comprehensive RHEED Image Library (RIL) for reference and further analysis.
kSA 400
The kSA 400 is the most advanced, full featured RHEED data acquisition and analysis package available. With a long list of capabilities, and available plug-in options, the kSA 400 offers the most insight from RHEED patterns. The kSA 400 RHEED analysis software has camera control options; data acquisition modes; acquisition, image analysis, data analysis, and export capabilities; and data storage and communications options.
kSA 400 Lite
A RHEED acquisition and analysis package for those requiring only basic image capture and data analysis. The kSA 400 Lite package can be upgraded to the full featured version of kSA 400 at any time. The kSA 400 Lite RHEED analysis software has full camera control features; pared down data acquisition modes; acquisition, image analysis, data analysis, and export capabilities; and data storage and communications options.
kSA 400 AOS
An Analysis Only version designed for users who want to perform post-acquisition display, processing, and analysis away from the laboratory. The RHEED analysis-only software (kSA 400 AOS) license is available to users who currently own a full kSA 400 system.
What You Get With a kSA 400 System
- High resolution, high S/N camera
- Optic Mounts for mounting to the RHEED screen viewport
- Appropriate cabling
- kSA 400 or kSA 400 Lite software for the Win10 operating system
- kSA 400 RHEED Image Library (full version of kSA 400 only)
- Computer (optional)
The kSA 400 supports several plug-in options to give you even more analytical capability. These plug-ins include:
- Electron Gun Control
- LEED IV (Low Energy Electron Diffraction)
- PLE (Phase-Locked Epitaxy)
- Rotation Monitoring and Triggering
- Auger/XPS Acquisition
These options can be added to a standard kSA 400 system at any time, and typically include a software plug-in and hardware additions. One of our most popular plug-in options is RHEED Electron Gun Control, which allows you to control all the settings of your RHEED gun through the kSA 400 software. The kSA 400 software also allows you to acquire RHEED images while varying gun control parameters e.g. beam rocking acquisition which is supported on Staib beam rocking electron guns.
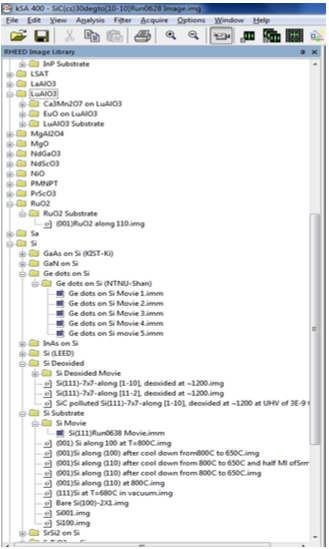
The kSA 400 RHEED Image Library (RIL) is a compilation of images and movies acquired from our kSA 400 customers, to the tune of ~ 30 gbytes of data. We have asked our customers to document the details of the conditions under which the data was taken, e.g. what the growth conditions are (temperature substrate, etc.), what the crystal orientation is, what the beam energy is, and so on. These details are either in the file name or in the Comments section of the file
We envision the use of the RIL to be mainly as a reference library for RHEED. Here are some examples of how we envision the RIL being used:
- You’re curious about what the oxide desorption process looks like for a GaAs substrate, so you load a GaAs desorb movie from the RIL and watch the evolution of the RHEED pattern as the oxide desorption occurs.
- You are working with SrTiO3 substrates, and you’d like to compare your RHEED patterns to those other researchers in your field are checking, for example, the width and length of the diffraction streaks as an indication of surface quality.
- You are teaching a surface science class and are on the topic of RHEED, and you’d like the students to check the ratio of lattice spacings along different crystal directions to verify the bcc structure of a material. You have the students pull up a GaAs movie, identify the major pull crystal directions (rotating substrate movie), and have them check the ratios of pixel spacings.
- You’d like to see what the growth of Ge quantum dots on Si looks like via RHEED.
- You’d like to look at GaAs on GaAs RHEED oscillations, and test our growth rate algorithms (we have 3 different algorithms in the kSA 400) on this movie data.
Optional kSA 400 accessories include:
- The highest quality RHEED screens. We supply P43, P31, or P48 (fast) phosphor screens, full or partial coat for standard and o.d. viewports. We can also re-coat existing screens. All screens are X-ray attenuating glass, and have a thin aluminum layer for grounding and stray light reflection. Optional stainless steel screen holders that mount inside standard zero profile viewports are also available.
- Beam-Alignment Substrates. For determining RHEED beam placement on the substrate, k-Space also provides 1″, 2″ and 3″ diameter Si substrates coated with P43 phosphor and silicate treated for smear resistance. UHV compatible.
- Laser Trigger Module (LTM). The LTM (Laser Trigger Module) product was developed by k-Space to meet the needs of scientists and engineers who desire an accurate trigger source coupled to a rotation stage during thin-film deposition. With the Laser Trigger Module, the user can program a single, precise trigger position during sample rotation to initiate external events such as acquiring images or making measurements at a specific rotation angle. By using a simple laser and high speed photo detector assembly mounted near the sample rotation shaft, rotation speeds up to 1500 rpm can be properly tracked and utilized within any kSA product to define a specific measurement position. Custom mounting brackets are typically required for individual needs and can be manufactured at additional cost.
- Rotation Monitoring and Triggering. The Rotation Monitoring and Triggering (RMAT) system has been developed by k-Space to provide an accurate, programmable triggering solution for synchronizing metrology equipment to sample rotation during thin-film deposition. The package seamlessly integrates a 12-bit absolute encoder and programmable logic controller (PLC) with user-friendly Windows-based software to provide four programmable trigger outputs that can be used to initiate measurements at specific rotation positions.
If you have any questions, do not hesitate to contact one of our Technical Sales Engineers.
References
View All ReferencesTransformation of the Elemental Composition on the GaN Surface During a 2D-3D Transition
Y.E. Maidebura, V.G. Mansurov, T.V. Malin, K.S. Zhuravlev
Cation reordering instead of phase transitions: Origins and implications of contrasting lithiation mechanisms in 1D ζ- and 2D α-V2O5
Yuting Luo, Shahed Rezaei, David A. Santos, Yuwei Zhang, Joseph V. Handy, Luis Carrillo, Brian J. Schultz, Leonardo Gobbato, Max Pupucevski, Kamila Wiaderek, Harry Charalambous, Andrey Yakovenko, Matt Pharr, Bai-Xiang Xu, and Sarbajit Banerje
Evolution of the Atomic and Electronic Structures During Nitridation of the Si(111) Suface Under Ammonia Flux
Vladimir Mansurov, Yury Galitsyn, Timur Malin, Sergey Teys, Denis Milakhin, Konstantin Zhuravlev
Engineering ordered arrangements of oxygen vacancies at the surface of superconducting La2CuO4 thin films
Y. Eren Suyolcu, Georg Christiani, Patrick T. Gemperline, et al.
Nanoscale-Resistive Switching in Forming-Free Zinc Oxide Memristive Structures
Roman V. Tominov, Zakhar E. Vakulov, Nikita V. Polupanov, Aleksandr V. Saenko, Vadim I. Avilov, Oleg A. Ageev, and Vladimir A. Smirnov
Substitution of Phosphorus at the InP(001) Surface Upon Annealing in an Arsenic Flux
Dmitriev, D.V., Kolosovsky, D.A., Fedosenko, A. I. Toropov & K. S. Zhuravlev